What Is Diabetes?
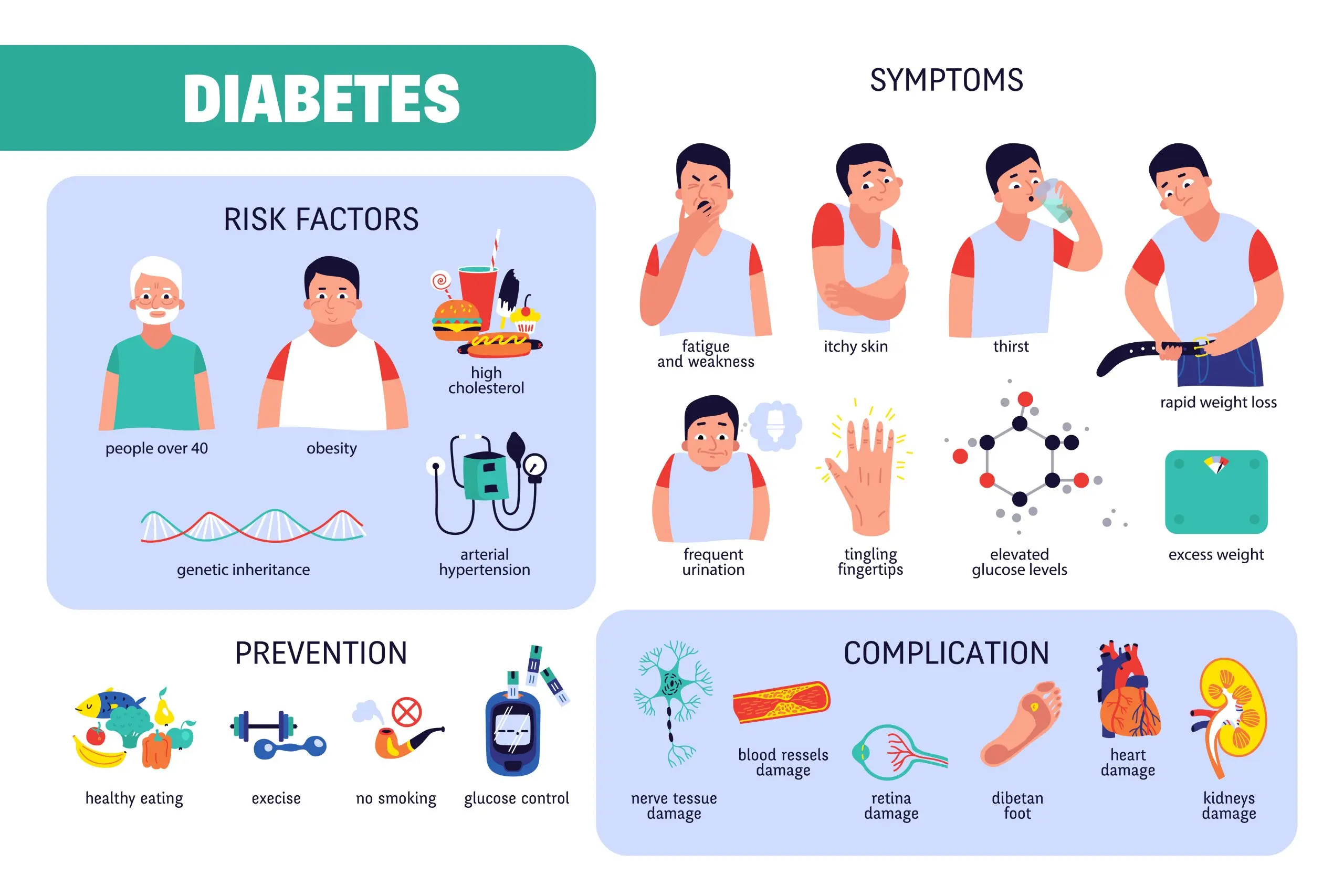
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. Without proper insulin function, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to various health issues.
Causes of Diabetes
The causes of diabetes vary depending on the type. However, some common factors include:
- Genetics – Family history increases the risk.
- Obesity – Excess weight is a significant risk factor, especially for Type 2 diabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle – Lack of exercise can lead to insulin resistance.
- Poor Diet – High intake of processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Autoimmune Response – In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
- Caused by: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells.
- Common in: Children and young adults.
- Treatment: Requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Caused by: Insulin resistance due to genetics, lifestyle, or obesity.
- Common in: Adults, though cases in children are rising.
- Treatment: Lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
Gestational Diabetes
- Caused by: Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Common in: Pregnant women, usually resolves after childbirth.
- Treatment: Diet, exercise, and sometimes insulin.
Prediabetes
- Caused by: Higher-than-normal blood sugar but not high enough for Type 2 diabetes.
- Common in: Adults at risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment: Lifestyle changes to prevent progression.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Recognizing early symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
| Common Symptoms | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent urination | ✅ | ✅ |
| Excessive thirst | ✅ | ✅ |
| Unexplained weight loss | ✅ | ❌ |
| Fatigue | ✅ | ✅ |
| Blurred vision | ✅ | ✅ |
| Slow healing wounds | ✅ | ✅ |
| Numbness in hands/feet | ❌ | ✅ |
Diabetes Treatment Options
1. Medications and Insulin Therapy
- Type 1 Diabetes: Requires daily insulin injections or an insulin pump.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Managed with oral medications (such as metformin) and sometimes insulin.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Diet: A low-carb, high-fiber diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Losing 5-10% of body weight can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
3. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
New technology allows people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels in real-time using a small sensor, reducing the need for frequent finger pricks.
Diabetes Prevention Tips
While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes can often be managed through lifestyle changes:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables.
- Exercise regularly to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
- Monitor blood sugar levels if you have risk factors for diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious but manageable condition with the right knowledge, lifestyle changes, and medical care. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals take control of their health. If you or a loved one experience diabetes symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Would you like additional information on specific treatments or diet plans? Let us know how we can help!
